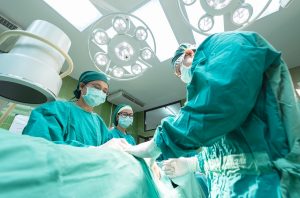
by Payton | Nov 19, 2018 | General
On July 5, 1996, the most renowned sheep in history was born, which also marked a breakthrough in scientific technology. Ian Wilmut and a group of Scottish scientists announced that they had successfully cloned a sheep named Dolly. Though the newly cloned sheep served as a significant scientific breakthrough, it also caused major controversy over the future and evolution of cloning (Bonsor and Conger). Since 1996, the science behind cloning has advanced, but cloning still creates religious and ethical disputes. Some say that cloning is against God’s plan for humanity and also abuses the laws of nature (Jackson), but cloning also has many profound medical benefits.
Cloning Procedure
The process suspect for human cloning is called somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), which is the method used to create Dolly. Somatic cell nuclear transfer involves doctors removing an egg cell from a female donor. The doctors then remove its nucleus, thus creating an enucleated egg. Another cell, which contains DNA, is taken from the organism being cloned. Scientists then fuse the enucleated egg and the subject’s cell with electricity. Once the cells fuze, an embryo is created. Doctors then implant the embryo into a surrogate mother through in-vitro fertilization (Bonsor and Conger).
History
Cloning is a popular topic in science-fiction literature. However, the idea of cloning has been around for a long time. The first data found on the concept of cloning dates back to approximately 40 years ago. Furthermore, in 1952, scientists cloned frogs from asexual tadpole cells. Furthermore, in 1997, scientists in Scotland successfully cloned Dolly the sheep, which brought cloning technology into the spotlight (McGee).
Medical Advancements
Stem Cells
Cloning provides great medical advancements via stem cells. These specialized cells can develop into any cell type in the body. This talent is what makes them the stars of regenerative medicine research. The industrial goal of cloning is to grow stem cells to produce new tissues and organs for patients suffering from various diseases. With today’s technology, scientists can alter adult cells to create single-use pluripotent cells that have the ability to differentiate into different types of cells. These cells are called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) (McGee).
Reproductive Assistance
Additionally, cloning can benefit medical advances and patient care in the healthcare industry. One of the most likely uses is as a method of assisted reproduction. Infertility affects approximately 10-15% of couples of the reproductive age throughout the developing world. However, the widespread introduction of assisted reproductive technologies has resulted in a high number of pregnancies and births that otherwise could not have occurred.
On the other hand, some people may not be able to find success in these methods possibly due to the absence of sperm or egg cells. The only options for these individuals are sperm donation, oocyte donation, adoption, surrogate mothers or reproductive cloning. Couples and individuals who wish to bear a child who has their DNA must utilize reproductive cloning to have success. Assisted reproductive cloning could also be used by individuals or couples who do not wish to reproduce by traditional means. By using cloning technology, couples or individuals can solve infertility or reproduce with minimal genetic input from another party (Zavos).
Therapeutic Cloning
Another medical use for cloning technology is therapeutic cloning. Cloning could be used to create tissues immunologically identical to an existing individual. In therapeutic cloning, genetic material from and the adult cell is placed inside an egg to grow beneficial stem cells. This procedure does not produce a baby. Instead, scientists seek to use the stem cells to generate necessary organs for transplant independently. They can also increase our understanding of development and the origins of disease (Barglow).
For more information, visit our website https://dynagrace.com/.
References
Barglow, Raymond. “Therapeutic Cloning Can Save Lives.” 2002. Document.
Bonsor, Kevin and Cristen Conger. How Stuff Works: How Human Cloning Will Work. 26 May 2013.
Jackson, Wayne. “Ethics of Human Cloning, The.” Document.
McGee, Glenn. “The Ethics of Human Cloning: An Overview.” 2001. Document.
Zavos, Panayiotis. “Reproductive Cloning is Moral.” 2002. Document.
Picture Resources: Featured Image: https://pixabay.com/en/dna-string-biology-3d-1811955/, https://pixabay.com/en/sheep-sheep-s-wool-wool-animal-345691/, https://pixabay.com/en/baby-child-cute-dad-daddy-family-22194/, https://pixabay.com/en/care-diagnose-disease-health-3031259/

by Payton | Nov 12, 2018 | General
California’s Three-Strikes Law came into effect in March 1994 with the purpose of decreasing the number of violent re-offenders. The law mandates imprisonment for a minimum of 25 years for offenders found guilty of a third felony. In a sense, this law operates as, “Three strikes and you’re out.” While the first two offenses must be serious felonies, the third can accrue to be any type of felony (Greenwood, et al., 1994). To combat the law, Stanford University created the Stanford Prison Advocacy Project. They provide unique services for those affected by the Three-Strikes Law such as litigation and research.
Advantages
Stanford Law School’s Justice Advocacy Project was created to combat the Three-Strikes Law through a variety of methods. However, their most impactful initiatives involve direct contact with the offenders. The project provides legal aid to represent those sentenced to life for minor crimes under the Three-Strikes Law and pursue civil rights impact cases regarding prison conditions and mandatory minimums. It also is a key component to develop criminal justice reforms to reduce sentences for non-violent crimes, such a Proposition 36 (Stanford Law School, 2018).
Furthermore, their Ride Home re-entry program provides services to released offenders to assist them in acclimating back into society. One of these services is access to re-entry counselors. These counselors are all reformed inmates. Visitation with these counselors is meant to decrease recidivism rates (Stanford Law School, 2018).
In addition to programs, they also provide cutting-edge research that gives Stanford Law School students valuable experience. This experience allows Stanford to continue their movement with the next generation of lawyers. Their research is meant to push the legal boundaries and influence policymakers to provide equal protection and rights for individuals convicted under the Three-Strikes Law (Stanford Law School, 2018).
Proposition 36
Due to public outrage to the Three-Strike Law, Congress passed Proposition 36 (Prop 36) in November of 2012. Prop 36 changed the sentencing requirements, so third-strike offenders were only subject to imprisonment for a minimum of 25 years if they are found guilty of a third violent felony. Therefore, offenders who were serving time due to non-violent third-strikes received a reduced sentence. Furthermore, the law treated them as if they only had two strikes (The Judicial Branch of California, 2018)
Furthermore, a study conducted in 2013 found that Prop 36 resulted in the release of over 1,000 inmates. Moreover, less than 2% re-offended with new crimes, which is below state and national recidivism rates. The release of inmates led to financial advantages by saving taxpayers in California between and $10 and $13 million (Aleaziz, 2014).
Disadvantages
Many critics of Stanford Law School’s Justice Advocacy Project believe that it obstructs investigations and frees violent offenders too soon. Rates of violent crimes in California increased by approximately 4% from 2015 to 2016 (Thompson, 2018). Moreover, property crime and violent crimes increased by 8% in 2017. Police found that habitual offenders committed most of the offenses (Harvard Kennedy School, 2018).
Furthermore, critics claim that the Stanford Law School’s Justice Advocacy Project is discriminatory in their services. They claim that it provides fewer and lower quality services to minority individuals and those suffering from mental disorders. Further claims say that they favor individuals of higher socioeconomic classes in their programs and services (Ghosn, 2015).
Utah
While Utah does not have a formal three-strike law, it does have provisions that exponentially increase the penalties for habitual offenders. According to Utah Code 76-3-203.5, an offender that has been found guilty and convicted of two violent felonies is subject to an enhancement in their punishment when convicted of a third violent felony (Utah State Legislator, 2013). This can lead to a first-degree level sentence for a felony that would classify as a third or second-degree under normal circumstances. Furthermore, if the first offense was a first-degree felony, then probation can be revoked. Furthermore, the individual’s standing as a habitual offender plays a key role in parole decisions (Canyon’s Law Group, 2018). Also, unlike California, Utah does not have an established advocacy program to ensure equality for these offenders.
Domestic violence offenses in Utah are treated similarly to the Three-Strikes Law. In these cases, enhancements are made to the offender’s punishment after one prior charge of domestic violence within a five-year period (Utah State Legislature, 2018).
For more information, visit our website https://dynagrace.com/.
References
Aleaziz, H. (2014, April 4). Study Says Inmates Released Under Prop. 36 Have Low Recidivism Rate. Stanford Law School Press.
Canyon’s Law Group. (2018, January 2). Does Utah Criminal Law Have a Three-Strikes Rule? Retrieved from Canyon’s Law Group: http://www.howarddefense.com
Ghosn, A. (2015, February 25). The Pitfalls of California’s Three Strikes Law. The Stanford Daily.
Greenwood, P. W., Rydell, C. P., Abrahamse, A. F., Caulkins, J. P., Chiesa, J., Model, K. E., & Klein, S. P. (1994). Three Strikes and You’re Out: Estimated Benefits and Costs of California’s New Mandatory Sentencing Law. RAND, 1-85.
Harvard Kennedy School. (2018, April). Recidivism and Reentry. Retrieved from Prison Policy Initiative: https://www.prisonpolicy.org
Stanford Law School. (2018). Stanford Law School. Retrieved from Three Strikes & Justice Advocacy Project: https://law.stanford.edu
The Judicial Branch of California. (2018). California’s Three Strikes Sentencing Law. Retrieved from California Courts: The Judicial Branch of California: California’s Three Strikes Sentencing Law
Thompson, D. (2018, April 9). Groups Debate if California has Gone too far on Crime Reform. The Sacramento Bee.
Utah State Legislator. (2013). Habitual Violent Offender. Retrieved from Utah State Legislator: https://le.utah.gov
Utah State Legislature. (2018, March 22). Enhancement of Offense and Penalty for Subsequent Domestic Violence Offenses. Retrieved from Utah State Legislature: https://le.utah.gov
Picture Resources: Featured Image: https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/File:Stanford_Oval_May_2011_panorama.jpg, https://pixabay.com/en/justice-statue-lady-justice-2060093/, https://pixabay.com/en/prison-jail-detention-fence-wire-370112/, https://pixabay.com/en/government-utah-utah-state-1410372/

by Payton | Nov 5, 2018 | General
Mental and physical health problems are more prominent in prison populations in comparison to the general public. On average, inmates have significantly higher rates of chronic diseases and illnesses such as hypertension, asthma, arthritis, cervical cancer, and hepatitis (Binswanger, Krueger, & Steiner, 2009). Furthermore, mental healthcare problems are consistently more prevalent in prison populations. The strict prison subculture is exceptionally detrimental to individuals suffering from these diseases (Birmingham, 2003). Overall, prisoners receive a lower quality of mental healthcare even though the court mandates equality.
Lack of Medications
In prison environments, adequate healthcare is usually only reserved for those who have severe mental or physical illnesses and injuries. Furthermore, treatment is dependent on resource availability and demand. Over 50% of the prisoners who underwent pharmacotherapy for mental diseases before being incarcerated did not receive medication in prison. The lack of treatment can have severe consequences such as rehabilitation failure, recidivism, or even death (Reingle Gonzalez & Connell, 2014).
Quality of Care
In addition, studies show that prisoners generally receive a lower quality of care because they are not considered paying customers. This status provides little incentive for prison healthcare providers to offer a high quality of care. Furthermore, approval to perform necessary tests and surgical procedures is a lengthy process that often is received after the prisoner has been transferred or released. Additionally, many prisoners have accused practitioners and nurses operating in prisons of avoiding crucial procedures and surgeries that have a high cost to the public (Awofeso, 2005). These decisions are often based on political views in regards to prisoners as well as a means of budgeting their expenses (Asch, et al., 2006).
Furthermore, many prisoners claim that the prison system hinders their ability to voice their health concerns. National health surveys often ignore inmates, so the public is vastly unaware about the prison population’s overall health. This exclusion also creates a skewed perception of disease and illness precedence in prisons (Awofeso, 2005).
State Prison Expenditures
The main focus on the prison system is to provide a reformative environment for the inmate so they can learn from their past and become a thriving citizen upon release. Prisons provide a location where these people can learn and grow while maintaining the safety of the general public. However, upholding the same level of security and care within prison facilities is essential to the reform process. Overall, the average amount of money that each state spends each year per prisoner is $33,274. Furthermore, approximately 11% of the total money spent goes towards healthcare needs. To serve as a point of comparison, 68% of prison expenditures provide for personnel salaries (Vera Institute of Justice, 2015). With the low amount of funding, healthcare has little effect on the overall prison operations.
For more information, visit our website https://dynagrace.com/.
Works Cited
Asch, S. M., Kerr, E. A., Keesey, J., Adams, J. L., Setodji, C. M., Malik, S., & McGlynn, E. A. (2006, March 16). Who Is at Greatest Risk for Receiving Poor-Quality Health Care? New England Journal of Medicine, 354, 1147-1156.
Awofeso, N. ( 2005, July 30). Making Prison Health Care More Efficient: Inmates Need More Organised and More Preventive Health Care in Emptier Prisons. National Center for Biotechnology Information, 331(7511), 248–249.
Binswanger, I. A., Krueger, P. M., & Steiner, J. F. (2009, July 30). Prevalence of Chronic Medical Conditions among Jail and Prison Inmates in the United States Compared with the General Population. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
Birmingham, L. (2003, May 9). The Mental Health of Prisoners. BJPsych Advances, 3, 191-199.
Ginn, S. (2012, September 17). Prison Environment and Health. British Medical Journal, 345.
Reingle Gonzalez, J. M., & Connell, N. M. (2014, December). Mental Health of Prisoners: Identifying Barriers to Mental Health Treatment and Medication Continuity. Am J Public Health, 104(12), 2328–2333.
Vera Institute of Justice. (2015). Prison Spending in 2015. Retrieved from Vera Institute of Justice: https://www.vera.org
Picture Resources: Featured Image: https://pixabay.com/en/prison-jail-detention-fence-wire-370112/, https://pixabay.com/en/capsule-pill-health-medicine-1079838/, https://pixabay.com/en/surgery-hospital-doctor-care-1807541/, https://pixabay.com/en/dollar-currency-money-us-dollar-499481/

by Payton | Oct 29, 2018 | General
Halloween is easily my favorite holiday. The many universal traditions involved with the holiday make Halloween both fun and unique. Some familiar rituals include carving pumpkins, searching for the perfect costume, trick-or-treating, decorating homes in spooky décor, or going through spook alleys. However, these traditions have ancient European and paganistic roots. Join Dynagrace Enterprises on our unique Halloween-themed blog on the history of common Halloween traditions.
The Date of October 31st
In 609 A.D., Christian leader, Pope Boniface IV, declared May 13th “All Martyrs Day.” This holiday persisted for nearly 200 years until the eighth century when Pope Gregory III declared that the celebration failed to recognize saints. He then mandated November 1st be a holiday celebrating all martyrs as well as saints. This holiday became known as “All Saints Day.” However, the new holiday overlapped with the Celtic New Year on the same day. The Celts had superstitious beliefs and would fill the holiday night with bonfires and chants to ward off evil spirits.
With the holidays on the same day, the principles and ideas behind them merged. Since the Celts believed that November 1st marked the end of summer and the beginning of the dark and deadly winter, the holiday became based on the idea that the veil between life and death was at its thinnest the day before the winter months began. This ideology meant that spirits could travel to the world of the living for one night. This new holiday on the 31st of October became known as Samheim or Holy Eve.
As the European ethnic groups meshed, Halloween became more commonplace. Now, the holiday is marked with numerous parties, people dressed in costumes, and ghost stories to celebrate the undead.
Iconic Halloween Colors
Based on ancient Celtic rituals, November 1st marked the end of the year and beginning of the cold and deadly winter. Many impoverished people died during the winter months because of the low temperatures and the lack of food. However, once warmer weather rolled along, poverty-stricken citizens could plant seeds and grow their harvest. The transition of seasons is the reason behind the classic Halloween hues of black and orange. Celts designated black to symbolize the terrible winters, and orange signified the hope and life associated with the summer months.
The Name “Halloween”
The term “Halloween” is thought to have originated in Scotland. It derived from the term “Holy Eve” which refers to the day before the Celtic New Year. In 1783, Glasgow poet John Main referred to the holiday as “Hallow-E’en” in his poem. His poetry became so immersed in the Celtic culture that the populace quickly defined October 31st as Hallow-E’en in replacement of Samheim or Holy Eve.
Jack-O-Lanterns
According to old Irish legend, there once existed a man named Stingy Jack who tried to cheat the devil. He repeatedly hunted and imprisoned Satan until he agreed not to send Stingy Jack to Hell when he died. While he successfully avoided going to Hell, he never found his place in Heaven. According to the lore, God barred Stingy Jack from entering the gates of Heaven, so Jack was doomed to straddle both Heaven and Hell or eternity. As a punishment, the devil cursed him to roam the earth forever using a hollowed turnip as a lantern.
Initially, people carved turnips and placed them in their windows to scare away “Jack of the Lantern” as well as other evil spirits. However, as immigrants came to America, they discovered that pumpkins make even better Jack-O-Lanterns.
Costumes
Wearing costumes on Halloween also has Celtic roots. During Samhain, they believed that the dead walked among the living. They also claimed that the evil spirits sought to harm the populace. However, ghosts couldn’t hurt their kind. Therefore, to protect themselves, they wore animal skin costumes that they thought disguised them as spirits. These costumes allowed them to hide in plain sight.
Trick-or-Treating
Throughout Samhain, the Celts had food offering that served to ward off evil spirits. However, some people began dressing up as ghosts to take advantage of the free food. These devious behaviors helped fuel the trick-or-treat culture.
Furthermore, in the Middle Ages, Christians would celebrate All Saints Day, and the poor would go “souling.” Souling is when individuals would visit a house and offer to say prayers for the family’s dead relatives in exchange for food. These food sacrifices became known as “soul cakes.”
As Halloween became more prevalent in America in the 19th century, the holiday took on a mischievous aspect. Instead of equal exchanges, it became more extortive by implying, “Give us treats, or we will prank you.” This new mindset is how the phrase “Trick or treat” came to be. However, vandalism grew rampant with this mindset, so, in the 1930’s, the communities encouraged the fun trick-or-treating traditions and atmosphere that we have today.
For more information, visit our website https://dynagrace.com/.
Resources: https://www.rd.com/culture/chilling-history-of-halloween-traditions/, https://www.thestreet.com/lifestyle/holidays-events/history-of-halloween-14735477, https://www.history.com/topics/halloween/history-of-halloween
Picture Resources: Featured Image: https://pixabay.com/en/moon-night-full-moon-gespenstig-703538/., https://pixabay.com/en/jack-o-lanterns-lit-pumpkins-3735386/, https://pixabay.com/en/halloween-trick-or-treat-pumpkin-1773447/, https://pixabay.com/en/ghost-black-and-white-dark-horror-1280683/, https://pixabay.com/en/pumpkin-lady-halloween-1713381/

by Payton | Oct 22, 2018 | General
With over 4.2 billion users surfing the internet, it may seem nearly impossible to protect your sensitive information from hackers and thieves. Devices connected to the internet often house our personal and professional lives. If a cyber criminal compromised this sensitive information, there could be disastrous consequences. However, the government dedicated the month of October as Cybersecurity Awareness Month in 2004 to educate internet users on how to navigate the web safely.
Cybersecurity Awareness Month
During October, the United States Department of Homeland Security and the National Cyber Security Alliance provide easily accessible information and tips to all netizens on how they can protect themselves online. The campaign is vital because it gives everyone in the cyberspace tools and knowledge to thwart cybercriminals. Although society is quickly shifting to a more digitalized world, it is surprising that the majority of users are blissfully unaware of the threats they can encounter online. Sharing too much information on social media sites, sending unencrypted personal information electronically, and making purchases on unsafe websites are common ways that criminals gain access to sensitive information.
“While the speed at which technology and information move can expose us to new risks online, it also enables a level of sharing and cooperation that can make us more resilient to cyber threats… National Cybersecurity Awareness Month isn’t just about understanding the risks, but also emphasizing our collective power to combat them.” – FBI Cyber Division Assistant Director Matt Gorham.
Furthermore, basic cyberattacks on personal devices can give criminals access to large businesses and organizations. For example, a hacker gained access to an employees computer information that eventually led to a cybersecurity breach against the United States Office of Personnel Management. The attack cost the company $21.5 million. Therefore, it is imperative that every individual takes proper cybersecurity precautions.
Results
As the government further educates internet users on cybersecurity risks, people are installing more security software. The number of software downloads increased significantly since 2004. Additionally, more cybercriminals are being reported and convicted. For example, the government arrested a cyber criminal who attempted to access university databases, 74 arrests of members of the overseas transnational criminal networks and a North Korean regime programmer who conspired to conduct multiple damaging cyber attacks resulting in extensive data and money loss, hardware destruction, and the loss of other resources.
With increased awareness, internet users can stay safe and protect their private information. Cybersecurity is a responsibility that lies on everyone’s shoulders. If we all fulfill our duty, we can significantly decrease the number of information breaches.
For more information about cybersecurity, visit our website https://dynagrace.com/.
Resources: https://www.normantranscript.com/opinion/happy-cyber-security-awareness-month/article_2864473b-205f-51c1-b06a-a793e2ffb5c9.html, https://www.fbi.gov/news/stories/ncsam-2018, https://www.army.mil/article/211977/keep_info_safe_during_cyber_security_awareness_month, https://www.wombatsecurity.com/cybersecurity-awareness-month?utm_term=%2Bcyber%20%2Bsecurity%20%2Bawareness%20%2Bmonth&utm_campaign=Security+Awareness+Month&utm_source=adwords&utm_medium=ppc&hsa_acc=8253056476&hsa_net=adwords&hsa_cam=1566723829&hsa_ad=295401163184&hsa_kw=%2Bcyber%20%2Bsecurity%20%2Bawareness%20%2Bmonth&hsa_grp=60967832564&hsa_mt=b&hsa_ver=3&hsa_src=g&hsa_tgt=kwd-368130389969&gclid=Cj0KCQjw6rXeBRD3ARIsAD9ni9DBJ8oOpYn7F2kz2M5GzZfQUn5qnX-DKgeh8mJkvHtEdgtNDSPMCfQaAvIeEALw_wcB
Picture Resources: Featured Image: https://www.flickr.com/photos/79061493@N04/10442488614/in/photostream/, https://www.flickr.com/photos/conquest-uk/30363339915/, https://www.flickr.com/photos/theboeingcompany/8090236600/

by Payton | Oct 15, 2018 | General
In a digitalized society, the importance of having top-notch cybersecurity has never been more crucial. Cyber-attacks can destroy businesses, reveal sensitive information, and drain your finances. Additionally, according to a new publication, they can also cause mass destruction and death. Recently, an audit by the Government Accountability Office (GAO) of the U.S. military’s newly developed weaponry systems revealed that they have critical cyber vulnerabilities. These security holes allow hackers easy access to control all of the U.S.’s computerized weapons systems. Furthermore, these findings indicate that, while the military prioritized the development of weapons, they failed to focus on the cybersecurity.
The Audit
The government conducted an audit from 2012 to 2017 that focused on their developing weaponry systems. They utilized skilled, friendly hackers to probe the Pentagon’s online networks for security holes and weaknesses. After releasing their findings this past Tuesday, the results are shocking. The hackers discovered carelessness and negligence in nearly all developing weapons systems. These security vulnerabilities allowed them to easily access the country’s military weapons through online means. Furthermore, in their reports, they stated that they were able to take control of entire systems, view the operator’s computer screens, and delete and add data. As a joke, they even flashed pop-up messages on the operator’s computer screens telling them that they needed to insert quarters before proceeding.
Moreover, while these results are startling, the agency warned that the reported problems represented a small fraction of the overall cyber vulnerabilities in the Defense Department.
What Caused the Security Vulnerabilities?
The GAO listed negligence to fundamental cybersecurity practices as the primary cause of the vulnerabilities. One typical example they saw was using default passwords. In one instance, the team of hackers took a total of nine seconds to guess an administrator’s security password.
“Due to this lack of focus on weapon systems cybersecurity, DOD likely has an entire generation of systems that were designed and built without adequately considering cybersecurity. . . Bolting on cybersecurity late in the development cycle or after a system has been deployed is more difficult and costly than designing it in from the beginning.” –GAO report
Past Reports
This report remains one of many warning the government of deficient cybersecurity. In 1996, the GAO brought cybersecurity vulnerabilities to the public’s attention. Additionally, in 2004, they notified the Pentagon that connecting military systems through the Internet also opened the door to hackers.
Furthermore, while the Pentagon issued a report that they are improving their security standards in response to the audit, many people question their sincerity. In one of the past assessments, the Pentagon only corrected 1 out of 20 identified vulnerabilities.
Threats of Digitalization
As a society, we tend to transition physical objects onto online networks so they can be controlled and operated online. In the government’s case, they digitally transitioned the control of weapons and spent approximately $1.6 trillion developing the new system. While online controls are convenient for us, it also opens the door to the possibility of hackers gaining control of these objects and using them to hurt or kill others.
On the other hand, digitalizing the weaponry system has allows the Pentagon to increase their military capabilities beyond what they could have imagined. For example, the F-23 Joint Strike Fighter is connected to millions of digital coding lines that allow it to activate and target areas. While using multiple codes as a safeguard is a great idea, it only truly protects others if it has cybersecurity against hackers.
For more information about cybersecurity, visit our website https://dynagrace.com/.
Resources: https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2018/10/10/nearly-all-new-us-weapons-systems-have-critical-cyber-security-problems-auditors-say/?noredirect=on&utm_term=.9da3d54db4ff, https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/economy/defense-industry-grapples-with-cybersecurity-flaws-in-new-weapons-systems/2018/10/14/b1de3bae-ce36-11e8-a360-85875bac0b1f_story.html?utm_term=.c77ebadd1d0e, https://sputniknews.com/us/201810141068879069-us-cyber-security-pentagon-risks/, https://thehill.com/policy/cybersecurity/411232-watchdog-exposes-pentagons-cyber-struggles?amp
Picture Resources: Featured Image: https://pixabay.com/en/f-35a-lightning-ii-fighter-jet-2657514/, https://pixabay.com/en/pentagon-washington-dc-military-80394/, https://pixabay.com/en/internet-cyber-network-finger-3589685/, https://pixabay.com/en/internet-security-password-login-1952019/