by Dr. Jane Fitzgerald | Jun 17, 2023 | Business, Data Science
The Truth About Data Scientists.
Data science is the latest buzzword in the business sector. Everyone, from business professionals to beginners, is talking about it. Data science is one of the most popular and promising career paths for skilled and up-to-date professionals.
So, what the heck is data science in business?

Image Credit: Flickr
Traditionally, data science is researching, collecting/acquiring, and analyzing a vast volume of data, including data mining and data programming skills. Data scientists are skilled professionals that organize and analyze a vast amount of data for businesses/organizations.
Since the dawn of the 21st century, data science has evolved far beyond its traditional threshold. Rapid changes in modern business management with regards to the birth of the internet motivates organizations to uncover more useful information, stay competitive, and ensure customer satisfaction. Organizations must learn how to improve functions and optimize processes through data science. The only way data-scientists can make this possible is by mastering every stage, making up the data science life-cycle.
Five Stages of the Data Science Life-Cycle
Data scientists seeking to deliver results in an insightful, understandable, and compelling way must be efficiently skilled in every stage.
Technically, there are five stages in the life cycle, and these are:
Stage #1. Capture
Under this stage, data scientists must be vast and efficient in data acquisition/collection, professional in data entry, skilled in signal reception, and data extraction.
Stage #2. Maintain
Skill sets required for this stage include data warehousing, good knowledge of data cleansing, effective data staging, excellent data processing skills, and data architecture.
Stage #3. Process
At this stage, the data scientist initiates data mining, and then proceed to cluster/classification. The last two-know-how skills required in this stage are data modeling and data summarization.
Stage #4. Analyze
This phase requires extreme exploratory/confirmatory data analytic skills, and expertise in predictive analysis, solid regression skills, text mining, and superb qualitative analysis.
Stage #5. Communicate
Communication is the last stage of the life cycle. The skill sets the data scientist is expected to have here are;
a. Data reporting (vital to organizations in meeting their overall goals and objectives),
b. Data visualization (a roadmap for businesses module implementation), and lastly,
c. Business intelligence and decision making for an overall business drive.
How Does Data Science Impact a Business?
Businesses use data science to improve product quality and day-to-day operations diagnostically.
Data scientists with high-level technical skills help businesses identify vital questions and collect
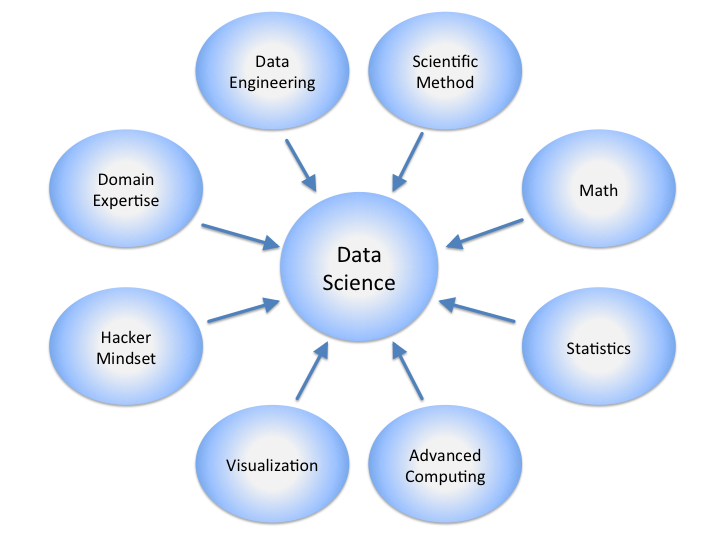
Image Credit: Wikimedia
data from multiple data sources. Next, they organize the information obtained, and translate the extracted results into actionable solutions, and communicate the same to management for positive business decisions.
These positive skills account for why data scientists have become prominent and sought after in all industries. Their ability to build and analyze algorithms with strong programming knowledge, quantitative skills in linear algebra and statistics, plus excellent communication skills makes them the knight in shining armor for any organization.
The vitality of data scientists in modern business practice cannot be overemphasized.
Data science and data scientists are a crucial aspect of every business setup in the 21st century. They do not just help businesses achieve their operational, strategic, and financial goals, but also help optimize acquisition, growth, and retention in customer success through the information it provides.
However, poorly utilized data science provokes huge financial loss in an organization.
Conclusion
Data scientists have the power to shape how organizations conduct business in line with customers’ changing needs and the rapid development of technology. There is a growing need for data scientists in the business sector. The job is ranked as the best profession in the United States for three consecutive years—2016-2018—and still growing. Also, the demand for experts in data science has increased by 28% in 2020, and from all indications, there is a sign of it slowing down soon.
by Dr. Jane Fitzgerald | Jun 17, 2023 | Artificial Intelligence, Emerging Technology, General, Information Technology
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a computer-controlled entity’s ability to perform cognitive tasks and respond flexibly to

Image Credit: Piqsels.com
its environment to increase the probability of achieving a specific goal. The program can learn from data, from experience, and can mimic actions similar to human beings. But it does not generally use biologically measurable methods.
AI describes the computer’s ability to execute tasks to accomplish the desired objectives. It also means that a computer can effectively reduce or even eliminate human activities.
Popular examples of chess, go, and dota intelligence demonstrates computers in certain areas and outperform human capabilities. Natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms are currently the most known fields for AI.
Types of AI
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
- Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
AGI is still a concept of theory, recognized as Ai with a human-level cognitive capacity in a broad range of fields, including language processing, image processing, computational functioning, reasoning, etc.
We’re quite a long way from AGI system development. The AGI program will need to involve thousands of tandem-working artificial narrow systems that interact with one another to mimic human thought. Also, in advanced computing systems and facilities such as Fujitsu’s K or IBM ‘s Watson, a single second of neural activity simulates within 40 minutes. It applies to immense complexity and interconnections between the human brain and the scale of the task of constructing an AGI with the current resources.
What is Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)?
ANI is the most popular type of AI on the market now. Such AI systems are designed to solve a single problem and can perform one function very well. They have limited capabilities by design, such as recommending a product for e-commerce users or weather prediction. It is today’s only form of artificial intelligence. They can approach human functioning in particular situations and, even in many cases, surpass it. But only in highly controlled environments with a limited range of parameters.
What is Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)?
Here we are almost into science fiction, but ASI alias as the logical development of AGI. An Artificial Super Intelligence system (ASI) could exceed all human capacities; this will involve decision-making, sound decisions, and even issues like improving the art and developing interpersonal ties.
When Artificial General Intelligence succeeds, AI systems could quickly boost their ability and push into fields that we could not foresee. While the distance between AGI and ASI is relatively narrow (some say just like a nanosecond because that is how quickly Artificial Intelligence will learn), the long path to AGI itself looks like a dream far into the future.

Image Credit: Wikimedia
What is the Purpose of AI?
Artificial Intelligence aims to aid human performance and help us make high-level decisions with far-reaching consequences. That’s the response from a technical standpoint. From a philosophical viewpoint, Artificial Intelligence can help humans lead more fulfilling lives free of hard labor and help manage the vast network of interconnected individuals, businesses, states, and nations to work in a manner that’s beneficial to all humanity.
Currently, Artificial Intelligence aims to simplify human effort and to help us make better choices by all the different tools and techniques that we have invented. Artificial intelligence, similarly marketed as our Last Innovation was a development that would create breakthrough technologies and services. It would also transform our way of life exponentially and eventually eradicate conflict, injustice, and human stress.
That’s all in the far future, though – we’re quite a long way from those kinds of outcomes. At present, the primary purpose of AI is to improve companies’ process efficiency, automate resource-intensive tasks, and produce business predictions based on hard data rather than good feelings. As with other technology, companies and government agencies must finance research and development expenses before they are available to laypeople every day.
The application of AI?
AI is used in different fields to provide insights into user behavior and to provide data-based recommendations. For example, the predictive search algorithm used by Google previous user data to predict what a user would type in the search bar next. Netflix uses past user data to decide what movie a user wants to see next, link the user to the app, and maximize watch time. Facebook uses previous users ‘ data to automatically suggest tagging your friends based on their facial characteristics in their images. AI is used in large organizations to simplify the life of an end-user. In general, the applications of artificial intelligence will come under the category of data processing, including:
- Data filtering and search optimization to give the most relevant results
- Logical chains for if-then reasoning serves to execute command strings based on parameters.
- Pattern detection to recognize essential trends for useful insights in large datasets.
- Applied probabilistic models to predict future results
Why does it matter?
The Internet-enabled global communication for all and impressively changed our way of working, living, and interacting. With process automation, AI is supposed to do the same; this will affect the consumer sphere, but it will also influence more repetitive business processes or simple decisions.
Some of the effects most discussed would be autonomous driving, but analysis, customer service, regulation, legal, and management are fields in which AI can improve productivity significantly. This cross-industry influence makes it critical that nearly everyone participates in AI.
Where are we today?
Even though AI has been around for over 50 years, we are still in the early stages. Factors such as processing power, worldwide networking, and cloud technology have just begun to open up artificial intelligence opportunities.
With the large enterprise data sets available – massive data hype, the three main phases of artificial intelligence segments into pattern recognition. The second phase currently involves commercializing deep learning algorithms, which enable real learning systems through neuronal networks. There are still a few years of abstract and reasoning intelligence, but its development is now beginning.
First experiments already were undertaken, but business applications currently focus on phase two-giving technology plenty of room for performance and adoption.

by Dr. Jane Fitzgerald | Dec 14, 2020 | Business, Data Science
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics is an inclusive term in the world of data science. It is the analysis of data collected from one or different sources. Trends, patterns, and correlations emerge from the analytics, which remains valuable for business practices.
Firstly, data analytics allows data scientists to gain insights through careful examination of datasets. Management teams use these insights to make informed and strategic business decisions towards future activities. Without data analytics, all data, no matter the size and derived source, is useless.
Secondly, when companies apply data analytics to any big data collected, they can efficiently improve customer service and increase sales turnover. Companies use this strategy to boost competitive performance.
Two Components of Data Analytics

Image Credit: Medium
Processing data analytics needs two critical elements for any data initiative to succeed. These are:
Descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics is the starting phase. It helps in describing historical and relevant trends found in the data. This analytics aims to answer the question of “what happened?”
It’s both a component and a type of analytics too.
As a component, descriptive analytics measures conventional indicators like Return on Investment (ROI). Such an indicator employed differs from industry to industry. Although descriptive analytics doesn’t make predictions or informed actionable decisions, it summarizes datasets in an expressive and meaningful way.
Advanced analytics
Here, the process uses advanced and innovative tools to extract relevant data, make appropriate predictions, and uncover trends.
Tools used in advanced analytics include, but are not limited to, machine learning and classical statistics. Machine learning tools like natural language conversion/processing, sentiment analysis, and neural networks, and more, generate new insight and info from data.
Advanced analytics focuses on the question of “What if?”
With the increasing popularity and use of large data sets, machine learning skills, and affordable computing power have made it easier to use these two data analytics techniques in different industries.
Four types of Data Analytics
Descriptive analytics

Image Credit: Medium
What the analytics seeks is the answer to the question, “what happened?” Under this technique, summarizing large datasets explains findings to all stakeholders. Descriptive analytics strategies help businesses to track successful performance or failures using KPI (key performance indicators) and metrics like ROI to gauge past performance.
Diagnostic analytics
Diagnostic analytics is the technique that seeks to answer why certain things happened. The process takes information from the descriptive-analytical level and further studies to unravel the root of the problem. Any performance indicator calls for more investigation to know why they got worse or better.
Predictive analytics
The predictive analytics technique focuses on events that would happen in the future. Using historical data, machine learning, and statistical methods, the study of patterns and trends tracks the possibility of reoccurrence. The outcome will be very valuable.
Prescriptive analytics
The presence of this technique offers solutions to the problem. By employing insights gotten from descriptive analytics, we gain inspired decisions. Also, it relies on machine-learning tactics capable of finding patterns in massive data sets.
Conclusion
Data analytics is a critical aspect of data science that data scientists should understand. Its application in everyday activities is almost endless. New business opportunities arise as a result of the continuous generation of data.
by Dr. Jane Fitzgerald | Dec 12, 2020 | Blockchain, Emerging Technology
Blockchain is an encrypted distributed database that records data. It can also be explained as a digital archive of all transactions and contracts that need to be registered independently. One of blockchain’s key advantages is that it is accessible through hundreds of thousands of computers and not limited to one location. The technology has already started to threaten the financial services market and also establishes the digital currency for a Bitcoin transaction.

Image Provided by Pixabay
With Blockchain technology in the financial sector, participants can interact directly and transact over the internet without third party interference; these transactions via blockchain do not share participant personal information and create a transaction record by encrypting identifying details. Blockchain’s most thrilling feature is that it significantly reduces the risk of a data breach. In contrast to traditional processes, multiple shared copies of the same database are present in the blockchain. This makes it difficult to perform any data violations attack or cyber attack. With all the characteristics that resist fraud, blockchain technology can revolutionize various business sectors and make processes more intelligent, secure, transparent, and efficient than traditional business processes.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
- Direct transactions that eliminate overheads and intermediary costs.
- Highly secure due to cryptographic and blockchain’s decentralized protocols.
- Increased time effectiveness due to real-time transactions.
- More transparent processes with proper record creation and tracking.
- Reduced risks related to cybercrimes, frauds, and tampering.
Applications of Blockchain Technology in Various Industries
Blockchain’s technology enhances many sectors such as Financial Services, Education, Government, Travel and Entertainment, Retail, and CPG.
Financial services
Blockchain technology, in many innovative ways, has already been implemented in the financial services sector. By offering an integrated trading lifecycle, blockchain technology simplifies and streamlines the entire process associated with asset management and payments, allowing all participants to access the same transaction data. It eliminates the need for brokers or intermediaries and guarantees accountability and effective transactional data management.
Healthcare
By increasing the privacy, security, and interoperability of the healthcare data, blockchain plays a crucial role in the medical sector. It can solve several interoperability challenges in the sector. The various organizations and people involved in the process can safely share data among themselves. By eliminating third-party intrusion, overhead costs decrease, and with secure encryptions, distributed databases store health records and digital signatures in blockchain to ensure confidentiality and authenticity.
Government
The technology of blockchain has the potential to change government processes and services. It can play a key role in improving data transaction challenges in the government’s current silo sector. The proper connection and sharing of data with blockchain allow better data management between several departments. It enhances transparency and strengthens transaction tracking and auditing processes.
CPG and Retail
The retail market could benefit greatly from Blockchain technology implementation. What the database will do is ensure that high-quality goods are genuinely authentic, prevent fraudulent transactions, find stolen items, enable virtual guarantees, manage loyalty points, and streamline supply chain operations.
Travel and hospitality
Blockchain’s application can change the travel and hospitality industry radically. Money transactions, storing key documents such as passports/other ID cards, reservations, and travel management, loyalty, and rewards can be processed through Blockchain.

Image Provided by Wikipedia
Key Challenges of using Blockchain Technology
Lack of understanding and knowledge of the technological concept are the main challenges of using it in non-financial services industries. The problems associated with the current legacy of corporate infrastructures and the lack of sufficient technological expertise are major barriers to blockchain’s widespread adoption. Adopting blockchain often means shifting culture from conventional ways of doing stuff, as it entails a significant change towards decentralizing the entire process. Compliance with current regulations and maintaining the privacy and protection needed for shared databases also adds to the key roadblocks in blockchain adoption.
The world of business will yet thoroughly explore the distinctions of the blockchain concept. Yet, we expect that the business world will soon see the vast potential of this technology with ongoing research and development in this field and to push a new wave of decentralized applications.

by Dr. Jane Fitzgerald | Oct 27, 2020 | Artificial Intelligence, Data Science, Industrial IoT
What is IIoT and its Link to Manufacturing?
The IIoT is part of a broader framework called the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT is a network of smart computers, devices, and objects that gather and share vast amounts of data. The data collected is sent to a central cloud-based service. Here, compiled with other data, end-users find it useful. IoT can improve the automation of homes, classrooms, stores, and many industries.
Implementing the IoT to the manufacturing industry refers to the IIoT (or Industrial Internet or Industry 4.0). It revolutionizes the production process, allowing much more data collection and storage at far higher speeds and far more effectively than before. A host of innovative companies began using smart connected devices in their factories to introduce the IIoT.
What are the Benefits of IIoT?

Image Credit: Wikimedia
For industrial organizations, the IIoT may significantly improve communication, performance, scalability, time savings, and cost savings. Because of predictive maintenance, improved safety, and other operational efficiencies, companies are already benefiting from it through cost savings. IIoT networks of intelligent devices enable manufacturing companies to break open data silos and connect their people, data, and processes from the factory floor to the executive offices. Business leaders can use IIoT data to provide a comprehensive and detailed insight into how their company is doing, which will help them make informed decisions.
Protocols
One of the issues encountered during the IIoT transition is that various edge-of-network devices have historically used different protocols to send and receive data. Many different communication protocols are currently in use, such as OPC-UA. The transfer protocol Message Queueing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is rapidly emerging as the standard for IIoT, due to its lightweight overhead, publish/subscribe model, and bidirectional capabilities. Read more on MQTT here.
Challenges
The two biggest challenges surrounding IIoT implementation are probably interoperability and security. As technology writer Margaret Rouse observes: “Industrial IoT is a major concern about interoperability between devices and machines that use different protocols and have different architectures.” For this, Ignition is an excellent solution because it is cross-platform and based on open-source, IT-standard technologies.
Companies need to know how secure their data is. The proliferation of sensors and other intelligent, connected devices led to a parallel explosion of security vulnerabilities; this is another factor in MQTT’s growth. It’s a very stable protocol.
The Future of the IIoT

The IIoT remains one of the fundamental phenomena that today and in the future impact industrial enterprises. Industries push for the modernization of systems and equipment to comply with new regulations, maintain increasing speed and volatility, and deal with disruptive technologies. Companies that have embraced the IIoT have seen significant improvements in safety, efficiency, and profitability. This trend will continue as the technologies grow widely.
The Ignition IIoT system significantly increases industrial organizations’ communication, performance, scalability, time savings, and cost savings. It can unite people and processes on the plant’s floor to those on the enterprise’s level. It also enables companies to get the most value out of their system without being limited by technological and economic constraints. For these and more reasons, Ignition offers the ideal forum for bringing IIoT’s power into your company.











